Search
2020–21 United States Senate special election in Georgia

The 2020–21 United States Senate special election in Georgia was held on November 3, 2020, and on January 5, 2021 (as a runoff), to elect the Class III member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Georgia. Democrat Raphael Warnock defeated appointed incumbent Republican Kelly Loeffler. The first round of the election was held on November 3, 2020; however, no candidate received a majority of the vote, so the top two candidates—Warnock and Loeffler—advanced to a runoff on January 5, 2021, which Warnock won narrowly.
The special election was prompted by Georgia Governor Brian Kemp’s appointment of Loeffler as the interim replacement for Republican Class III Senator Johnny Isakson, who resigned in December 2019. The winner of this election would serve a shortened term concluding on January 3, 2023. An election to serve a full six-year term was set for November 8, 2022.
In accordance with Georgia law, no primary election took place for the special election; all candidates, regardless of party, were placed on the same ballot (known as a nonpartisan blanket primary, or "jungle primary"), and the election was held on November 3, 2020. Warnock received the most votes with 32.9%, and Loeffler came in second with 25.9%. As no candidate received more than 50% of the vote, the top two candidates advanced to a runoff election on January 5, 2021.
The runoff was held concurrently with the regular Georgia Class II Senate election, in which Democrat Jon Ossoff defeated incumbent Republican David Perdue, also in a runoff on January 5. Following the November 3, 2020 Senate elections, Republicans held 50 Senate seats and the Democratic caucus—consisting of 46 registered Democrats and two allied independents—held 48. Because of this, the two Georgia runoffs determined the balance of the United States Senate under the incoming Biden administration. Winning both races gave the Democratic caucus 50 Senate seats, an effective majority with Democratic Vice President Kamala Harris casting tie-breaking votes. The extraordinarily high political stakes caused the races to attract significant attention nationwide and globally.
Major media outlets, including Decision Desk HQ, the Associated Press, The New York Times, and NBC News, called the election for Warnock in the early hours of January 6, just minutes after he apparently declared victory. Though Loeffler vowed to challenge the results after she returned from the electoral vote certification in Washington, she conceded on January 7. Ossoff and Warnock became the first Democrats to be elected to the U.S. Senate from Georgia since Zell Miller in the 2000 special election. Warnock is the first Black senator from Georgia, as well as the first Black Democrat from the South elected to the Senate. Though Warnock is the first Democratic senator from this seat since the latter election, hours later Ossoff was declared the winner in the regular Senate election. The two elections mark the first time since the 1994 United States Senate election in Tennessee and the concurrent special election that both Senate seats in a state have flipped from one party to the other in a single election cycle. This was also the first time the Democrats achieved this since West Virginia's 1958 Senate elections. The election results were certified on January 19, 2021, with the senators-elect taking office on January 20.
Background
On August 28, 2019, Isakson announced that he would resign from the Senate effective December 31 due to his deteriorating health. This triggered a special election to fill the remainder of his term. On September 17, Georgia Governor Brian Kemp launched a website inviting Georgia citizens to submit their résumés in order to be considered for appointment. President Donald Trump advocated the appointment of Representative Doug Collins. Kemp appointed Loeffler to fill the seat until the 2020 special election; she took office on January 6, 2020.
Candidates
Democratic Party
Despite the large number of candidates in the special election, by October 4, 2020, the Democratic Party had largely consolidated around Warnock's candidacy and had pressured other Democratic candidates, such as Matt Lieberman, to drop out to avoid vote-splitting.
While she had not been treated as a major contender, being largely ignored by pollsters, Deborah Jackson received 6.6% of the vote in the initial round of the election, being the second-best performing Democrat, and outperformed fellow Democrats such Matt Lieberman and Ed Tarver, who pollsters had paid attention to. Al Jazeera attributed her performance, in part, to her being the first Democrat listed in the order of candidates that appeared on the ballot, and her being a familiar figure in the Democratic stronghold of DeKalb County.
Advanced to runoff
- Raphael Warnock, senior pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church
Eliminated
- Deborah Jackson, attorney and former mayor of Lithonia
- Jamesia James, businesswoman and U.S. Air Force veteran
- Tamara Johnson-Shealey, businesswoman and frequent candidate
- Matt Lieberman, businessman, activist, and son of Joe Lieberman, former U.S. senator from Connecticut
- Joy Felicia Slade, physician
- Ed Tarver, former United States Attorney for the Southern District of Georgia and former state senator
- Richard Dien Winfield, professor and candidate for Georgia's 10th congressional district in 2018
Declined
- Stacey Abrams, nominee for Governor of Georgia in 2018 and former minority leader of the Georgia House of Representatives (endorsed Raphael Warnock)
- Sherry Boston, DeKalb County District Attorney
- Jason Carter, nominee for Governor of Georgia in 2014, former state senator, and grandson of former U.S. President Jimmy Carter (endorsed Raphael Warnock)
- Stacey Evans, candidate for Governor of Georgia in 2018 and former state representative (running for state house)
- Jen Jordan, state senator
- Lucy McBath, incumbent U.S. representative for Georgia's 6th congressional district (running for re-election)
- Michelle Nunn, CEO of CARE USA and nominee for U.S. Senate in 2014; daughter of former senator Sam Nunn.
- Jon Ossoff, documentary filmmaker and nominee for Georgia's 6th congressional district in 2017 (successfully ran for Class 2 seat)
- Mike Thurmond, DeKalb County chief executive, former Labor Commissioner of Georgia, and nominee for U.S. Senate in 2010
- Teresa Tomlinson, former mayor of Columbus (ran in the Democratic primary for the Class 2 seat)
- Nikema Williams, state senator and Chair of the Georgia Democratic Party
- Sally Yates, former United States Deputy Attorney General
Endorsements
Republican Party
Advanced to runoff
- Kelly Loeffler, incumbent U.S. Senator
Eliminated
- Doug Collins, incumbent U.S. representative for Georgia's 9th congressional district
- Derrick Grayson, minister, network engineer, software developer, perennial candidate, U.S. Navy veteran
- Annette Davis Jackson, businesswoman and candidate for Georgia State Senate in 2016
- Kandiss Taylor, student services coordinator for Appling County Board of Education
Withdrawn
- Ervan Katari Miller, perennial candidate
- Wayne Johnson, former chief operating officer of the Office of Federal Student Aid (remained on ballot)
Declined
- Nick Ayers, former chief of staff to Vice President Mike Pence
- Ashley Bell, regional administrator for the Small Business Administration
- Paul Broun, former U.S. representative for Georgia's 10th congressional district
- Buddy Carter, incumbent U.S. representative for Georgia's 1st congressional district
- Geoff Duncan, incumbent lieutenant governor of Georgia
- Stuart Frohlinger, finance expert
- Tom Graves, incumbent U.S. representative for Georgia's 14th congressional district
- Karen Handel, former U.S. representative and former Georgia Secretary of State (running for Georgia's 6th congressional district)
- Scott Hilton, former state representative (endorsed Loeffler)
- Jan Jones, Speaker pro tempore of the Georgia House of Representatives
- Brian Kemp, incumbent governor of Georgia (endorsed Loeffler)
- Butch Miller, state senator
- B. J. Pak, United States Attorney for the Northern District of Georgia and former state representative
- Sonny Perdue, United States Secretary of Agriculture and former governor of Georgia
- Tom Price, former United States Secretary of Health and Human Services and former U.S. Representative for Georgia's 6th congressional district
Libertarian Party
Declared
- Brian Slowinski, Republican candidate for Georgia's 10th congressional district in 2014
Green Party
Declared
- John "Green" Fortuin
Independents
Declared
- Al Bartell, businessman, former Republican and Vietnam-era Air Force veteran
- Allen Buckley, attorney, accountant, Libertarian nominee for the U.S. Senate in 2004, 2008, 2016 and nominee for Lieutenant Governor of Georgia in 2006
- Michael Todd Greene
- Rod Mack (as a write-in candidate), member of the City of Hapeville Board of Appeals and candidate in the 2018 Georgia gubernatorial election
- Valencia Stovall, state representative
Special election
Polling
Jungle primary
Predictions
Results
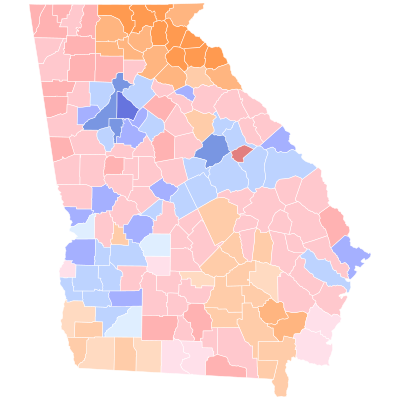
Since no candidate won a majority of the vote on November 3, the top two finishers—Loeffler and Warnock—advanced to a January 5, 2021 runoff election.
Results by congressional district
Loeffer won 7 out of 14 congressional districts to Warnock's 6 and Collins's 1.
Runoff
The runoff election for Isakson's former seat was on January 5, 2021. The regularly-scheduled runoff election for the Georgia U.S. Senate seat held by Republican David Perdue was also decided in a January 5 runoff. Before the Georgia runoffs in the 2020 U.S. Senate elections, Republicans held 50 Senate seats and the Democratic caucus held 48. Warnock declared victory on January 6, 2021. If Democrats won the other Georgia runoff held on January 5, their caucus would gain control of the Senate, as the resultant 50–50 tie would be broken by Democratic vice president-elect Kamala Harris. If they lost the second race, Republicans would retain control. The extremely high political stakes caused the races to attract significant attention nationwide. They were the third and fourth Senate runoff elections held in Georgia since runoffs were first mandated in 1964, after runoffs in 1992 and 2008. It was also the third time that both of Georgia's Senate seats have been up for election at the same time, following double-barrel elections in 1914 and 1932. The Associated Press and other major news outlets called the race for Warnock in the early morning hours of January 6. His win was attributed to heavy black voter turnout.
The deadline for registration for the runoff election was December 7. Absentee ballots for the runoff were sent out beginning on November 18, and in-person voting began on December 14.
Predictions
Polling
- Aggregate polls
Results
Results by congressional district
Despite losing, Loeffler won 8 of 14 congressional districts.
Republicans filed two federal and one state lawsuit in December to restrict the January 5 vote. On December 17, Judge Eleanor L. Ross found that plaintiffs lacked standing based on possible future harm to toss out a consent decree regarding signatures on absentee ballot applications. Judge James Randal Hall threw out another case which tried to block the use of drop boxes for absentee ballots. A third lawsuit, to restrict the use of drop boxes, was heard in state court on December 24.
On December 18, a federal judge threw out a Republican lawsuit alleging that out-of-state residents were voting in the runoff election, as Republican attorney Bill Price has recommended. Another lawsuit was filed against the use of voting machines manufactured by Dominion Voting Systems, alleging that election officials are handling mail-in absentee ballots improperly and illegally.
Judge Leslie Abrams Gardner, sister of Democratic politician Stacey Abrams, of the United States District Court for the Middle District of Georgia rejected the attempted purge of 4,000 voters in Muscogee County and Ben Hill County, Georgia, on December 29. The ruling means the voters were able to participate in the January 5 runoff election. The ruling was amended to allow provisional voting to prevent election-day challenges.
See also
- 2020–21 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2020 Georgia (U.S. state) elections
- 117th United States Congress
- List of special elections to the United States Senate
Notes
- Partisan clients
- Voter samples and additional candidates
- Miscellaneous
References
Further reading
- Amber Phillips (October 9, 2020), "The Senate seats most likely to flip parties in November", Washingtonpost.com
External links
- "Georgia 2020 Purge List", SaveMyVote2020.org, Los Angeles, CA: Palast Investigative Fund,
Check if you have been purged from the Georgia voter rolls
- "League of Women Voters of Georgia". January 5, 2018. (State affiliate of the U.S. League of Women Voters)
- Elections Archived November 12, 2008, at the Wayback Machine at the Georgia Secretary of State official website
- Georgia at Ballotpedia
- Government Documents Round Table of the American Library Association, "Georgia", Voting & Elections Toolkits
- National Institute on Money in Politics; Campaign Finance Institute, "Georgia 2019 & 2020 Elections", OpenSecrets
- Request a mail-in ballot at the Georgia Secretary of State website
- Check to see if you are registered to vote Archived November 10, 2020, at the Wayback Machine at the Georgia Secretary of State website
- Register to vote at Vote.org
- Official campaign websites
- Raphael Warnock (D) for Senate
- Kelly Loeffler (R) for Senate Archived January 7, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Doug Collins (R) for Senate Archived September 26, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- Deborah Jackson (D) for Senate
- Brian Slowinski (L) for Senate
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: 2020–21 United States Senate special election in Georgia by Wikipedia (Historical)
Articles connexes
- 2020–21 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2020 United States Senate elections
- 2020 United States Senate special election in Arizona
- 2022 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2020 United States presidential election in Georgia
- MeidasTouch
- 2016 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2020 United States Senate election in Alabama
- 2017 United States Senate special election in Alabama
- 2024 United States Senate elections
- 2022 United States Senate elections
- 2020 United States Senate election in Mississippi
- 2026 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2004 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2014 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2010 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 2020 United States Senate election in Delaware
- 1992 United States Senate election in Georgia
- 1820–21 United States Senate elections
- 1994 United States Senate special election in Tennessee
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou



