Search
Promethazine

Promethazine, sold under the brand name Phenergan among others, is a first-generation antihistamine, antipsychotic, sedative, and antiemetic used to treat allergies, insomnia, and nausea. It may also help with some symptoms associated with the common cold and may also be used for sedating people who are agitated or anxious, an effect that has led to some recreational use (especially with codeine). Promethazine is taken by mouth (oral), as a rectal suppository, or by injection into a muscle (IM).
Common side effects of promethazine include confusion and sleepiness; consumption of alcohol or other sedatives can make these symptoms worse. It is unclear if use of promethazine during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe for the fetus. Use of promethazine is not recommended in those less than two years old, due to potentially negative effects on breathing. Use of promethazine by injection into a vein is not recommended, due to potential skin damage. Promethazine is in the phenothiazine family of medications. It is also a moderate anticholinergic, which produces its sedative effects. This also means high or toxic doses can act as a deliriant.
Promethazine was made in the 1940s by a team of scientists from Rhône-Poulenc laboratories. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1951. It is a generic medication and is available under many brand names globally. In 2021, it was the 188th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions. In 2021, the combination with dextromethorphan was the 289th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 600,000 prescriptions.
Medical uses
Promethazine has a variety of medical uses, including:
- Sedation
- In Germany, it is approved for the treatment of agitation and agitation associated with underlying psychiatric disorders with a maximum daily dose of 200 mg.
- For nausea and vomiting associated with anesthesia or chemotherapy. It is commonly used postoperatively as an antiemetic. The antiemetic activity increases with increased dosing; however, side effects also increase, which often limits maximal dosing.
- For moderate to severe morning sickness and hyperemesis gravidarum: In the UK, Promethazine is the drug of first choice. Promethazine is preferred during pregnancy because it is an older drug and there is more data regarding the use of it during pregnancy. Second choice medications, which are used if Promethazine isn't tolerated or the patient cannot take it, are metoclopramide or prochlorperazine.
- For allergies such as hay fever and together with other medications in anaphylaxis
- To aid with symptoms of the common cold
- Motion sickness, including space sickness
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn
- Anxiety before surgery
- Short-term insomnia
Side effects
Some documented side effects include:
- Tardive dyskinesia, pseudoparkinsonism, acute dystonia (effects due to dopamine D2 receptor antagonism)
- Confusion in the elderly
- Drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, more rarely vertigo
- Known to have effects on serotonin and dopamine receptors.
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Respiratory depression in patients under age of two and in those with severely compromised pulmonary function
- Blurred vision, xerostomia, dry nasal passages, dilated pupils, constipation, and urinary retention. (due to its anti-cholinergic effects)
- Chest discomfort/pressure (In children less than 2 years old)
- Akathisia
Less frequent:
- Cardiovascular side effects to include arrhythmias and hypotension
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- Liver damage and cholestatic jaundice
- Bone marrow suppression, potentially resulting in agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia
- Depression of the thermoregulatory mechanism resulting in hypothermia/hyperthermia
Rare side effects include:
- Seizures
Because of potential for more severe side effects, this drug is on the list to avoid in the elderly. In many countries (including the US and UK), promethazine is contraindicated in children less than two years of age, and strongly cautioned against in children between two and six, due to problems with respiratory depression and sleep apnea.
Promethazine is listed as one of the drugs of highest anticholinergic activity in a study of anticholinergenic burden, including long-term cognitive impairment.
Overdose
Promethazine in overdose can produce signs and symptoms including CNS depression, hypotension, respiratory depression, unconsciousness, and sudden death. Other reactions may include hyperreflexia, hypertonia, ataxia, athetosis, and extensor-plantar reflexes. Atypically and/or rarely, stimulation, convulsions, hyperexcitability, and nightmares may occur. Anticholinergic effects like dry mouth, dilated pupils, flushing, gastrointestinal symptoms, and delirium may occur as well. Treatment of overdose is supportive and based on symptoms.
Pharmacology
Promethazine, a phenothiazine derivative, is structurally different from the neuroleptic phenothiazines, with similar but different effects. Despite structural differences, promethazine exhibits a strikingly similar binding profile to promazine, another phenothiazine compound. Both promethazine and promazine exhibit comparable neuroleptic potency, with a neuroleptic potency of 0.5. However, dosages used therapeutically, such as for sedation or sleep disorders, have no antipsychotic effect. It acts primarily as a strong antagonist of the H1 receptor (antihistamine, Ki = 1.4 nM) and a moderate mACh receptor antagonist (anticholinergic), and also has weak to moderate affinity for the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, D2, and α1-adrenergic receptors, where it acts as an antagonist at all sites, as well. New studies have shown that promethazine acts as a strong non-competitive selective NMDA receptor antagonist, with an EC50 of 20 μM; which might promote sedation in addition with the strong antihistaminergic effects of the H1 receptor, but also as a weaker analgesic. It does not however affect the AMPA receptors.
Another notable use of promethazine is as a local anesthetic, by blockage of sodium channels.
Chemistry
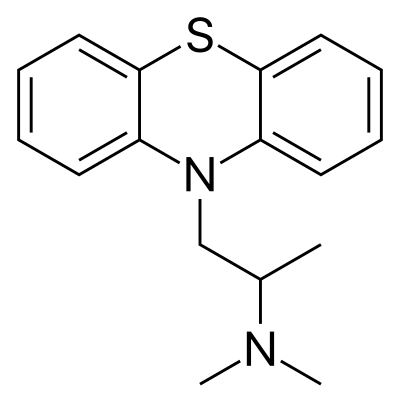
Solid promethazine hydrochloride is a white to faint-yellow, practically odorless, crystalline powder. Slow oxidation may occur upon prolonged exposure to air, usually causing blue discoloration. Its hydrochloride salt is freely soluble in water and somewhat soluble in alcohol. Promethazine is a chiral compound, occurring as a mixture of enantiomers.
History
Promethazine was first synthesized by a group at Rhone-Poulenc (which later became part of Sanofi) led by Paul Charpentier in the 1940s. The team was seeking to improve on diphenhydramine; the same line on medical chemistry led to the creation of chlorpromazine.
Society and culture
As of July 2017, it is marketed under many brand names worldwide: Allersoothe, Antiallersin, Anvomin, Atosil, Avomine, Closin N, Codopalm, Diphergan, Farganesse, Fenazil, Fenergan, Fenezal, Frinova, Hiberna, Histabil, Histaloc, Histantil, Histazin, Histazine, Histerzin, Lenazine, Lergigan, Nufapreg, Otosil, Pamergan, Pharmaniaga, Phenadoz, Phenerex, Phenergan, Phénergan, Pipolphen, Polfergan, Proazamine, Progene, Prohist, Promet, Prometal, Prometazin, Prometazina, Promethazin, Prométhazine, Promethazinum, Promethegan, Promezin, Proneurin, Prothazin, Prothiazine, Prozin, Pyrethia, Quitazine, Reactifargan, Receptozine, Romergan, Sominex, Sylomet, Xepagan, Zinmet, and Zoralix.
It is also marketed in many combination drug formulations:
- with carbocisteine as Actithiol Antihistaminico, Mucoease, Mucoprom, Mucotal Prometazine, and Rhinathiol;
- with paracetamol (acetaminophen) as Algotropyl, Calmkid, Fevril, Phen Plus, and Velpro-P;
- with paracetamol and dextromethorphan as Choligrip na noc, Coldrex Nočná Liečba, Fedril Night Cold and Flu, Night Nurse, and Tachinotte;
- with paracetamol, phenylephrine, and salicylamide as Flukit;
- with dextromethorphan as Axcel Dextrozine and Hosedyl DM;
- with dextromethorphan and ephedrine as Methorsedyl;
- with dextromethorphan and pseudoephedrine as Sedilix-DM;
- with dextromethorphan and phenylephedrine as Sedilix-RX;
- with pholcodine as Codo-Q Junior and Tixylix;
- with pholcodine and ephedrine as Phensedyl Dry Cough Linctus;
- with pholcodine and phenylephedrine as Russedyl Compound Linctus;
- with pholcodine and phenylpropanolamine as Triple 'P';
- with codeine as Kefei and Procodin;
- with codeine and ephedrine as Dhasedyl, Fendyl, and P.E.C.;
- with ephedrine and dextromethorphan as Dhasedyl DM;
- with glutamic acid as Psico-Soma, and Psicosoma;
- with noscapine as Tussisedal; and
- with chlorpromazine and phenobarbital as Vegetamin.
Recreational use
The recreational drug lean, also known as purple drank among other names, often contains a combination of promethazine with codeine-containing cold medication.
Product liability lawsuit
In 2009, the US Supreme Court ruled on a product liability case involving promethazine. Diana Levine, a woman with a migraine, was administered Wyeth's Phenergan via IV push. The drug was injected improperly, resulting in gangrene and subsequent amputation of her right forearm below the elbow. A state jury awarded her $6 million in punitive damages.
The case was appealed to the Supreme Court on grounds of federal preemption and substantive due process. The Supreme Court upheld the lower courts' rulings, stating that "Wyeth could have unilaterally added a stronger warning about IV-push administration" without acting in opposition to federal law. In effect, this means drug manufacturers can be held liable for injuries if warnings of potential adverse effects, approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), are deemed insufficient by state courts.
In September 2009, the FDA required a boxed warning be put on promethazine for injection, stating the contraindication for subcutaneous administration. The preferred administrative route is intramuscular, which reduces risk of surrounding muscle and tissue damage.
References
External links
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: Promethazine by Wikipedia (Historical)
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou