Search
10 Rockefeller Plaza

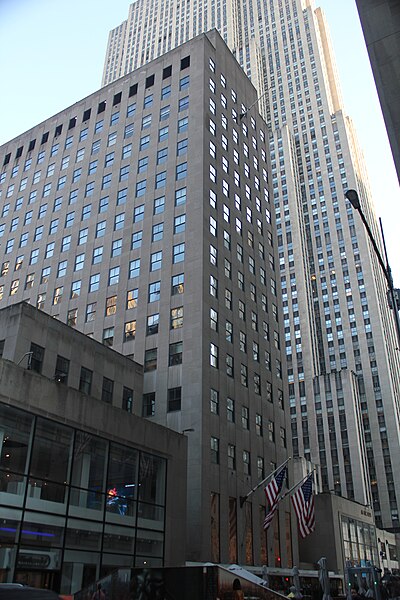
10 Rockefeller Plaza (formerly the Eastern Air Lines Building and Holland House) is a 16-story building located on Rockefeller Plaza between 48th and 49th Streets in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Completed in 1940, the building is part of Rockefeller Center and, like the rest of the complex, was built in the Art Deco style.
Architecture
10 Rockefeller Plaza is located on the west side of Rockefeller Plaza between 48th and 49th Streets. Its planning name was the Holland House, but the Dutch government did not sign on, so the building became the Eastern Air Lines Building instead.
Form and facade
10 Rockefeller was built as a 16-story slab, basically a miniature version of 1 Rockefeller Plaza across the street. Unlike the other buildings, there are no exterior reliefs or carvings on 10 Rockefeller Plaza.
The lowest four stories are designed as storefronts. There are four-story-tall glass-faced retail wings to the north and south, which contrast with the design of the rest of the complex. The northern wing contains a rounded moderne-style corner at Rockefeller Plaza and 48th Street. Instead of a limestone entrance portal, 10 Rockefeller had a glass portal with a large mural on the lobby wall behind it. The design of the glass-faced retail space was considered "baffling" to retailers, and the space remained unused until at least the 1950s.
The upper 12 stories contain offices. There is one setback on the facade, similar to that on 1 Rockefeller Plaza.
Features
The lobby includes a staircase that curves down to the shopping concourse underneath the entire Rockefeller Center complex. 10 Rockefeller Plaza contains one mural, The History of Transportation, created by Dean Cornwell in 1946. This mural is placed on the west wall of the lobby. The mural is made up of three parts: "Night Flight", "New World Unity", and "Day Flight". The piece depicts planes and gods flying at night; historical means of transport such as steamboat and steam train; and Rickenbacker's racecar, among other things. It is textured with gold and silver leaf, which respectively provide a contrast between "earthbound" and "airborne" motifs.
As stipulated in the original plans, the building also contains a six-floor parking garage with 800 spots, accessible from 48th Street. Garages in New York City office buildings had been prohibited under the 1916 zoning law until it was amended in 1935. As a result, 10 Rockefeller contained New York City's first garage in an office building, and the design of 10 Rockefeller's garage was unique for the area. There is a lounge for car owners, a recreational area for chauffeurs, and bronze firepoles for attendants to access the garage quickly.
A rooftop garden exists on the third floor, above the garage and retail space. There are two more tiers of gardens on the fifth and sixth floors. Notable modern tenants include the studios for NBC's Today and Nightly News programs, and, since 2005, the Nintendo New York store.
History
Development
Rockefeller Center occupies three blocks in Midtown Manhattan bounded by Fifth and Sixth Avenues to the east and west, between 48th Street to the south and 51st Street to the north. In early plans for the construction of Rockefeller Center, the site of 10 Rockefeller Plaza was supposed to have been occupied by a house for the Metropolitan Opera. The planned opera house was canceled in December 1929 due to various issues, and John D. Rockefeller Jr. negotiated with Radio Corporation of America (RCA) and its subsidiaries, National Broadcasting Company (NBC) and Radio-Keith-Orpheum (RKO), to build a mass media entertainment complex on the site. By May 1930, RCA and its affiliates had agreed to develop the site. Most of the complex had been completed by 1936. Rockefeller Center Inc. only needed to develop three empty plots in the middle of the complex's northern and southern blocks.
The final plot on the southernmost block needed to be developed, and several tenants were being considered. In spring 1937, the center's managers approached the Dutch government for a possible 16-story "Holland House" on the eastern part of the plot. A six-floor parking garage would fill the hard-to-lease space on the lowest three floors of the building, as well as three basement floors. The Dutch government did not enter the agreement because of troubles domestically, most notably Hitler's invasion of the Netherlands. However, Rockefeller Center's managers were already in negotiations with Eastern Air Lines, whose CEO Eddie Rickenbacker would sign a lease in June 1940. The Dutch government did move into temporary offices in the International Building.
Excavation started in October 1938, and the building was topped out by April 1939. Upon the Eastern Air Lines Building's completion, the Dutch government moved its offices-in-exile into the new building. The new structure was unique for its glass-wrapped lower facade and the lack of art over its doorways. Although the complex itself was finished in November 1939, the Eastern Air Lines Building was not officially complete until its dedication in October 1940.
Later years
Tishman Speyer, led by Jerry Speyer and the Lester Crown family of Chicago, bought Rockefeller Center's original 14 buildings and land in 2000 for $1.85 billion. In April 2023, Tishman Speyer proposed renovating ten of the building's upper stories into a 130-room hotel operated by Aspen Hospitality.
References
Citations
Sources
- Adams, Janet (1985). "Rockefeller Center Designation Report" (PDF). City of New York; New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 7, 2017. Retrieved December 15, 2017.
- Balfour, Alan (1978). Rockefeller Center: Architecture as Theater. McGraw-Hill, Inc. ISBN 978-0070034808.
- Krinsky, Carol H. (1978). Rockefeller Center. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-502404-3.
- Okrent, Daniel (2003). Great Fortune: The Epic of Rockefeller Center. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0142001776.
- Reynolds, Donald (1994). The Architecture of New York City: Histories and Views of Important Structures, Sites, and Symbols. J. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-01439-3. OCLC 45730295.
- Roussel, Christine (May 17, 2006). The Art of Rockefeller Center. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-3930-6082-9.
Text submitted to CC-BY-SA license. Source: 10 Rockefeller Plaza by Wikipedia (Historical)
Langue des articles
- anglais (english)
- français (french)
- espagnol (spanish)
- portugais (portuguese)
- italien (italian)
- basque
- roumain (romanian)
- allemand (german)
- néerlandais (dutch)
- danois (danish)
- suédois (swedish)
- norvégien (norwegian)
- finnois (finnish)
- letton (lettish)
- lituanien (lithuanian)
- estonien (estonian)
- polonais (polish)
- tchèque (czech)
- bulgare (bulgarian)
- ukrainien (ukrainian)
- russe (russian)
- grec (greek)
- serbe (serbian)
- croate (croatian)
- arménien (armenian)
- kurde (kurdish)
- turc (turkish)
- arabe (arabic)
- hébreu (hebrew)
- persan (persian)/farsi/parsi
- chinois (chinese)
- japonais (japanese)
- coréen (korean)
- vietnamien (vietnamese)
- thaï (thai)
- hindi
- sanskrit
- urdu
- bengali
- penjabi
- malais (malay)
- cebuano (bisaya)
- haoussa (hausa)
- yoruba/youriba
- lingala
Quelques articles à proximité
Owlapps.net - since 2012 - Les chouettes applications du hibou